Front-end Editor has a simple goal. Fewer trips to the backend editor, in both a…
Htaccess is the abbreviation for Hypertext Access, and it is basically a configuration file designed to control the Apache Web Server running the website. In fact, .htaccess is a very old configuration file. It was coded in the initial stages of the web (HTTP), for one of the first web servers. In time, the htaccess-configured web servers grew into the World Wide Web (www) that we all know and use today. It is still in use due to its effective abilities to password protect folders, redirect users to another page, and create and use custom error pages just to name a few.
.htaccess file is able to take precedence over many server configuration settings, thus it is often used for cache control, authorization, and URL rewriting. In WordPress, the .htaccess file is predominantly used for rewriting URLs, consequently making them appear comprehensible and approachable by people and search engines.
It is also worth emphasizing that its name begins with a period, and ends with “htaccess.” The person editing the .htaccess file must be careful; otherwise, they may end up with a .txt or .html extension.
Some web hosts do not permit editing the .htaccess file. In such cases, it is possible to create a .htaccess file and upload it to a specific directory. The .htacces file will then control the designated directories and its subdirectories.
.htaccess file is often used for redirecting the users to a custom error page, depending on the web server error they run into. Here, it is possible to use the custom error page to present the users with a list of the site’s top articles, a sitemap, or even the site’s navigation system. The custom error page can also highlight the FAQ, thus keeping the users on the website rather than having them leave and go back to the search engine.
Using the .htaccess file for redirecting the users to a custom error page is quite simple – if one knows the proper error code. The most commonly used ones are:
- 400 – Bad request
- 401 – Authorization Required
- 403 – Forbidden
- 404 – File Not Found
- 500 – Internal Server Error
In order to use .htaccess with these codes, it is necessary to open a text editor, create a new document, and specify the error message that will be redirected in the following way:
ErrorDocument 404 /filenotfound.html
Then the .htaccess file is saved (bearing in mind the obligatory extension) and uploaded to the web host’s required directory.
What is Htaccess Editor
In order to additionally simplify editing .htaccess files, we suggest using a free plugin called Htaccess Editor. The plugin has recently been taken over by WebFactory, so you can expect it to be regularly updated and always working as it should.
Nowadays, WP Htaccess Editor is a clean, reliable and straightforward plugin that enables a secure way to rewrite .htaccess files.
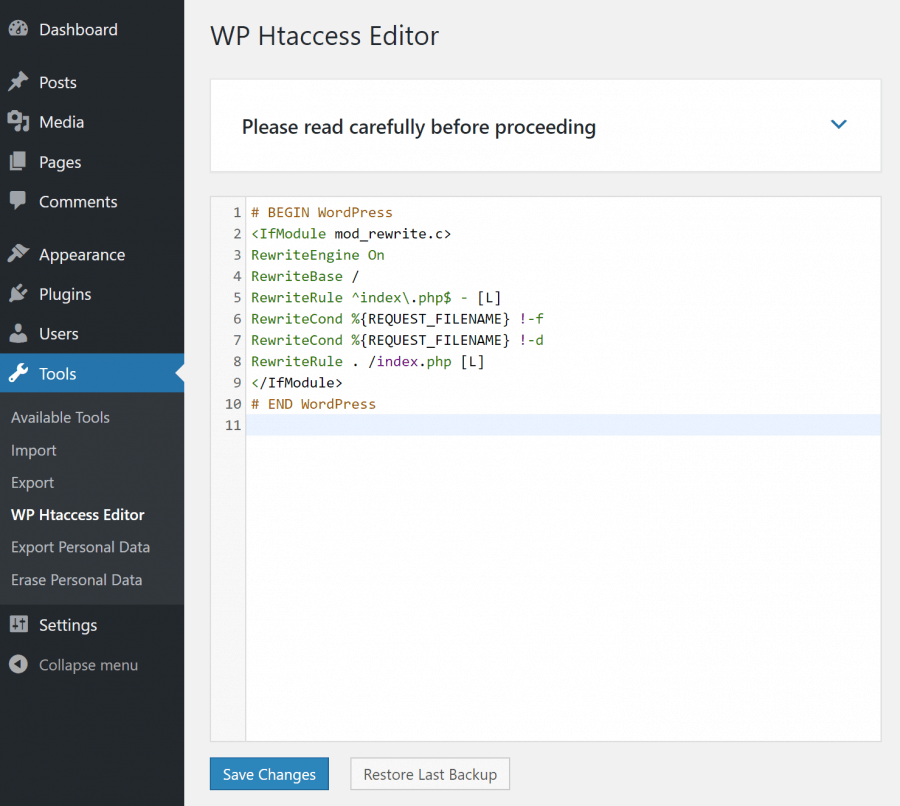
The plugin merely adds a new menu on the Admin control panel enabling the backup, restoring and editing the .htaccess files faster, while the WordPress core remains intact.
Htaccess Editor Installation
As with every plugin developed for WordPress, the installation is simplified and undemanding: it can be carried out automatically or manually.
For automatic installation, the admin opens the WordPress admin, and in the Plugins tab, selects Add New option. Then the admin types “htaccess editor” in search, clicks Enter, and the plugin will show up first on the list. After installing it, the admin can then activate and open its settings in the Tools menu.
For manual installation, it is necessary to download the latest version available here. The admin then unzips and uploads it to /wp-content/plugins/, opens the WordPress admin -> Plugins and clicks “Activate” located next to “WP Htaccess Editor”. Once this is completed, the plugin can be found on the plugin’s admin page under the Tools menu.
How Does It Work
It is quite frustrating to use the Web Cpanel or FTP client such as FileZilla every time when the .htaccess file editing is necessary.
Fortunately, the Htaccess Editor plugin is quite easy to use because it allows editing the .htaccess file directly from the WordPress dashboard. This feature is time-efficient as well.
The backup option is the biggest advantage in this plugin when compared to the other ways of file editing. Access to this file editor is simple because it is placed within the Tools > WP Htaccess Editor of the WordPress Administration. Here, on the right side of the Administration panel, the file can be edited. Thus finding the editing tool is extremely easy – it is placed a new menu on Admin control panel where it is possible to do a backup, restore and edit your .htaccess file much faster than FTP client does.
Additional Htaccess Editor Feature – Automatic Backup
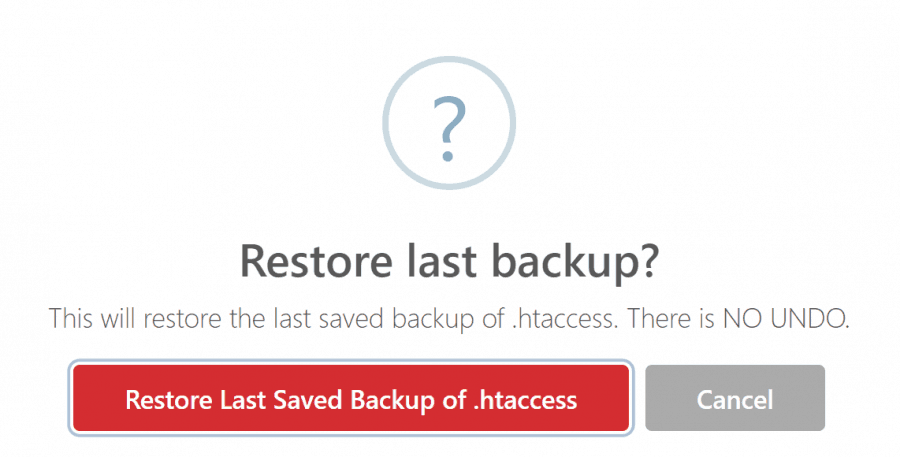
Beyond any doubt, the plugin best feature is an automatic backup – made every time a .htaccess file is edited. These backups remain available to the admin and can be restored from the plugin in case an error in .htaccess file blocks the site from running. The file backups can be found in /wp-content/htaccess-editor-backups/ and are timestamped so that the latest .htaccess backup can be easily found and restored.
Costs, Caveats, Etc.
The plugin is free. Since this plugin is already bug-free and with over 40,000 installations, 5-star rating and perfect reviews this is the most reliable plugin that will put you in charge of the behind-the-curtain activities on your site. Any questions that the users may have can be asked on the official forum.
Excellent support is available and the plugin is continuously updated and upgraded. The developers allow other contributors and developers to translate this plugin in local languages, so if you’re ready to help, don’t hesitate to leave a message.