Occasionally, this occurs – the need to completely reset WordPress. This is not a small undertaking, and it requires concentration and careful handling.
This article will lead you through the whole process, including the steps for manually resetting WordPress website, and the reasons why it may be necessary to do so.
The reasons for resetting WordPress
There may be several reasons for resetting WordPress, however the most common are:
- Restoring the website from a backup
- Rebuilding/ repurposing the website
- Cleaning out a test installation
In its most basic form, resetting a website means uninstalling the current settings and reinstalling the initial default settings. This also applies to all the files and databases – thus they are all returned to the default state. This can all be done by simply deleting everything. On the other hand, a partial reset is required and possible – the admin may need to reset the database but keep the plugins intact. Thus the steps for manual reset of the WordPress are described below.
How to reset WordPress
Basically, there are two ways to do so: with or without a plugin.
When resetting WordPress without a plugin, the admin goes by the following steps:
1. Deleting the database
This is the first step, and it is essential this is where all the contents and settings are located. The admin logs in cPanel and finds the list of MySQL databases in Databases->MySQL Databases
Here the list of the existing databases can be found. Some hosts prefer naming their databases but will include prefix wp in the database name.
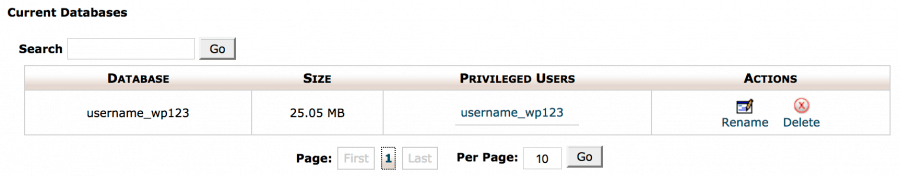
The admin can then copy and paste the name into a text file on a different safe location. It is then safe to delete this database by clicking on the delete button on the right side. This action completely deletes the database from WordPress.
2. Creating a new database
After deleting a database, it is essential to create a new one immediately. Otherwise, WordPress website will not be able to load and it will be impossible to access the dashboard and create any new content.
Thus, without leaving the cPanel database page, the admin goes on the Create a New Database, and inputs the database name so it matches the old, deleted one.
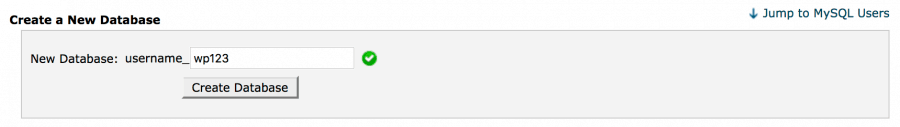
After entering the name and clicking Create Database, the page is automatically refreshed and the name appears again in the Current Databases area. The admin then goes on the Add a User to a Database and adds the old user with their permissions to the newly-created database. After that, he or she selects the matching database and username in the drop-down menus and clicks Add User.
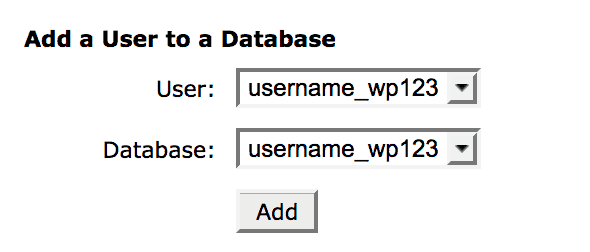
The admin may have to manually create a new user if they can’t find the old user. This is simply done within the Add a New User section. It is recommended to use the same username and password as the old database user, as this information can be found in the website’s wp-config.php file.
In the FTP software, the admin navigates to the website’s public_html folder. The WordPress root files are located there, and it is necessary to right-click on wp-config.php and choose View/Edit within the FTP program.

Here the admin does not have to edit anything but find the credentials for the old database user under MySQL Settings in the file.
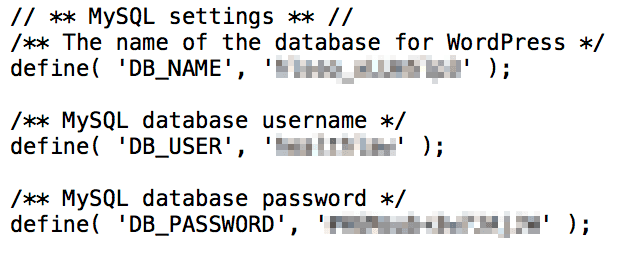
These credentials can be used to recreate the correct user in MySQL. It is vital to remember to follow the steps mentioned above and add the user to the database after creating it.
3. Remove Unnecessary Files
After deleting the database and creating a new clean one, all that is left are all the themes, plugins, files and other uploads which were added on the old website. It is recommended to remove these as well since the resetting of WordPress isn’t complete by simply deleting the database.
The majority of WordPress files remain the same, however, the admin must have added specific plugins, media, and themes for that website. All these additions are located in the wp-content folder.
These can be simply done via FTP – the admin logs in using the favorite FTP application navigates to the WordPress’ root directory under public_html, finds the wp-content folder and navigates inside. This is where all themes, uploads, and plugins folders are located. The admin should select every folder except themes and delete them all.

The admin then navigates inside the themes folder to choose the theme they would like to keep (for example, twentyseventeen), selects every theme folder except for the chosen theme, and deletes them from the server.

Now, all unique elements on the WordPress website have been deleted. The database is empty, and all unique files have been deleted.
The final step is to reinstall WordPress from scratch.
4. Run WordPress Installation Script
After deleting the database and all additional files, the website itself is not functional. In order for it to work, it is necessary to rerun the WordPress installation script. This will revert the WordPress back to its default settings.
The admin can load up the installation script by adding /wp-admin/install.php on the end of the domain name. A few settings will have to be made, such as language and the new login information.
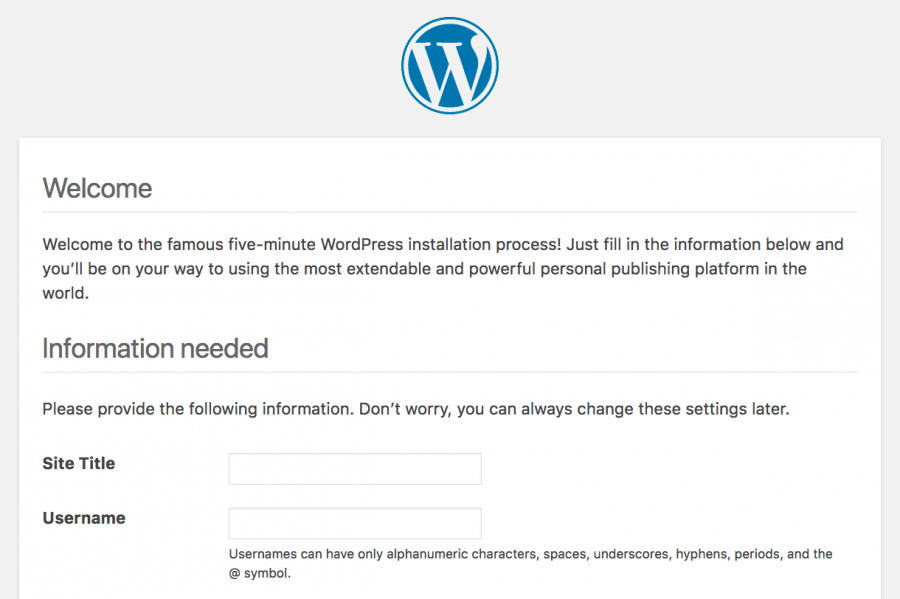
If the admin doesn’t run this script, WordPress will be unable to function. After completing the entire form, the admin can click Install WordPress, and the following message will appear:
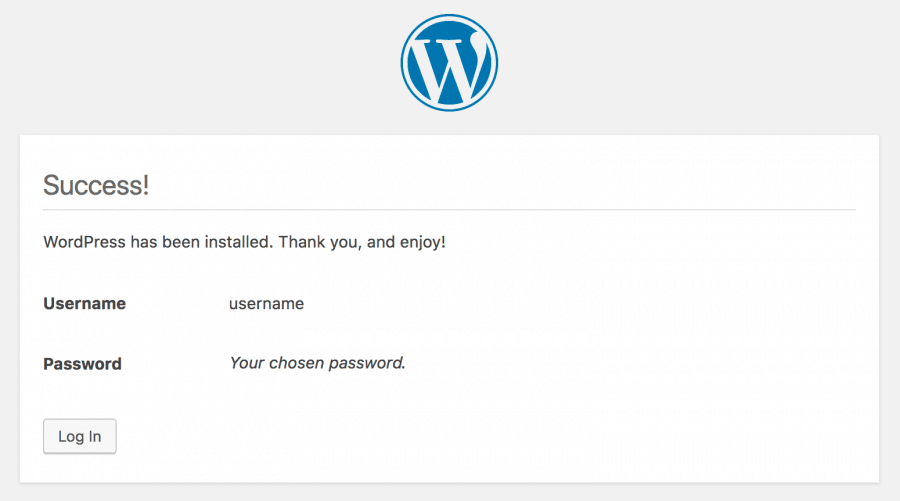
The admin can then click Log In and the new WordPress website is ready to run. This final step regains the admin’s access to the site and enables working with a clean slate.
Use WP Reset
Another option for resetting WordPress website mentioned above is resetting with a plugin.
Excellent plugin developed for this purpose is WP Reset. This is a simple and clean alternative to the above mentioned slow and difficult process of resetting a WordPress website. It is designed to reset the database to the default state, deleting the customizations and content without modifying the files. It has several fail-safe mechanisms safeguarding the data.
In comparison to the above mentioned step-by-step method, this plugin simplifies the whole process by miles. After installing the plugin, activating it, the admin simply navigates to Reset bar at the top of the WP Reset menu. The admin then scrolls on to the end of the page, and types in “reset” in the provided bar. The plugin is designed so to make the admin confirm the action one more time because there is no undo option. The admin is then automatically logged out, logged in and taken to the admin dashboard. WP Reset plugin can be reactivated if that option is chosen in the post-reset options.
Resetting with WP Reset deletes:
- default WP database tables
- custom database tables that have the same prefix table prefix as the one defined in wp-config.php and used by default tables
- media entries, posts, comments, pages, custom post types, users
Resetting with WP Reset does not delete nor modify:
- media files – they remain in the wp-uploads folder, however, they are not listed under Media in admin
- files: plugins, themes, uploads
- WordPress address; site title, address, and language; search engine visibility settings
- currently logged in user is restored with the current username and password
The plugin has excellent – partial reset tools:
- Delete transients – for all transient related database entries, as well as expired and non-expired transients,
- Delete uploads – for all files and folder in the /uploads/ folder
- Delete plugins – for all plugins, except WP Reset which remains active
- Reset theme options – for all options for all themes that use the WP theme mods API
- Delete themes – for all themes,
- Empty or delete custom tables – empties (truncates) or deletes (drops) all custom database tables
- Delete .htaccess file – for the .htaccess file.
The developers recommend the admins to be careful with multi-sites. Since the plugin has yet to be completely tested with multi-sites, the admins are advised against using WP Reset with the main site. Using the plugin with sub-sites has been tested and works flawlessly.
The developers and the support team are very active on the official WP Reset support forum. However, should the need arise for direct contact, it is also possible to write emails to wpreset@webfactoryltd.com.
Final thoughts
Resetting a WordPress website is demanding work, and not everyone has the time or energy to do so. However, it is a good skill to have for fixing broken websites and cleaning up unnecessary files. For those who have the courage to undertake this manually on their own without a plugin – kudos to you.
For the rest of us, who prefer a safe and easy way to handle this – we have to thank the people who develop the plugins such as WP Reset. Thank you for making this less painful.
